Introduction
PBPK models incorporate complex drug and system (ie, physiology) information into a mathematical framework to support dose selection while considering various patient factors (eg, age, sex, and comorbidity). Through "predict-learn-confirm cycles," PBPK models enable dose prediction to optimize clinical study design. BIVV001 (rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN), a new class of FVIII replacement therapy designed to break the von Willebrand factor (VWF) half-life ceiling (Chhabra et al.Blood. 2020; Konkle et al.Blood. 2018), consists of a single recombinant FVIII fused to dimeric Fc (to permit recycling of BIVV001 by a naturally occurring pathway via Fc neonatal receptors [FcRn]), a VWF D′D3 domain, and two XTEN® polypeptides (XTEN® is a registered trademark of Amunix Pharmaceuticals, Inc.). In a Phase 1 study (Lissitchkov et al.Blood. 2019), four once-weekly BIVV001 50 IU/kg infusions provided high sustained FVIII activity with a mean half-life of 41.3 hours. We aimed to build and verify an initial PBPK model to characterize BIVV001 activity levels in adults with severe hemophilia A.
Methods
To our knowledge, this is the first time that a PBPK model has been studied in hemophilia. We assumed that the distribution of BIVV001 and recombinant FVIII Fc fusion protein (rFVIIIFc) (Eloctate®) involves the FcRn recycling pathway that is similar to monoclonal antibodies. First, to evaluate the feasibility of the modeling approach, we built a PBPK model (Simcyp, Sheffield, UK) that captured FcRn-dependent recycling of Fc fusion proteins. Model input parameters were adjusted to capture observed rFVIIIFc activity levels with a prediction error of <1.35 by fitting values for the physiological parameters, equilibrium dissociation constant for FcRn binding (KD1), endothelial uptake rate (Kup), rate of recycling (Krc), and clearance by catabolism (CLcat). Next, a similar approach was used to characterize FVIII activity levels during the Phase 1 BIVV001 repeat-dose study (BIVV001 50 IU/kg and 65 IU/kg). The PBPK model virtual trial simulations were conducted at both BIVV001 doses using 100 virtual male subjects with an age range of 18-51 years.
Results
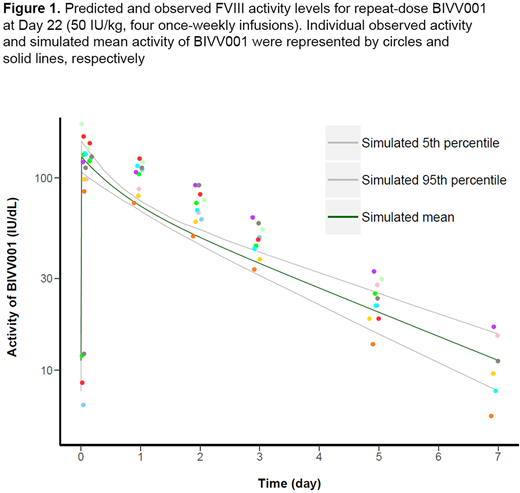
To fit the BIVV001 data, the PBPK model input parameters, KD1, vascular reflection coefficient (σv), and Kup, were modified compared with those used for the rFVIIIFc PBPK model. The PBPK model captured observed BIVV001 exposure with a low prediction error (<1.30) for maximal FVIII activity and area under the activity-time curve (Figure 1). The predicted inter-subject variability was lower than that for the observed data, which is likely due to the inability to include coefficients of variation for all parameters in the current Simcyp biologics module.
Conclusions
We have developed a PBPK model that accurately predicts the high sustained FVIII activity levels observed with BIVV001 exposure in adults with severe hemophilia A. The PBPK model framework can be a useful tool in the development of FVIII replacement therapies for hemophilia A.
Xia:Sanofi:Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.Katragadda:Sanofi:Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.Teutonico:Sanofi:Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.Macha:Sanofi:Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.Demissie:Sanofi:Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.Benson:Sanofi:Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal